As banks think about applying machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies, they have to remember that they have a responsibility towards their customers and society – all of this in a manner that’s transparent and traceable.
Banks are also answerable to their regulators, though regulations on technologies like AI is not in par with the developments in the industry. However, banks should look at this as a measure to uphold public trust, integrity and information quality, fairness and non-discrimination, and so on, which will play a significant factor in the bank’s reputational risk. In fact, banks, that are looking to be progressive in their adoption of AI technologies, should work with regulators to make sure regulation keeps up with industry adoption.
Trust in large companies is waning across the consumer segments. Companies like Facebook, for example, have had hefty fines that have been placed on them by regulators. In a recent lawsuit, Facebook was asked to pay a $5 billion (€4.43 billion) fine by US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to settle an investigation into its handling of user data and privacy lapses. Google was accused of abusing its market dominance in the search engine space giving unfair advantages to another Google product, its comparison shopping service. In June 2017, Google was fined €2.42 billion by European Commission for breaching EU antitrust rules.
Dealing with privacy
Adoption of AI technologies will involve managing and analysis of large amounts of data, a majority of which will involve privacy concerns. So to ensure banks treat customers fairly, they should look at measures such as hiring social scientists. These professionals will weigh in on some of the ethical and privacy concerns that organizations will have to face as they start exploring commercial applications leveraging AI. And this is not futuristic, it is already happening in companies like Google as we speak.
AI that is Ethical
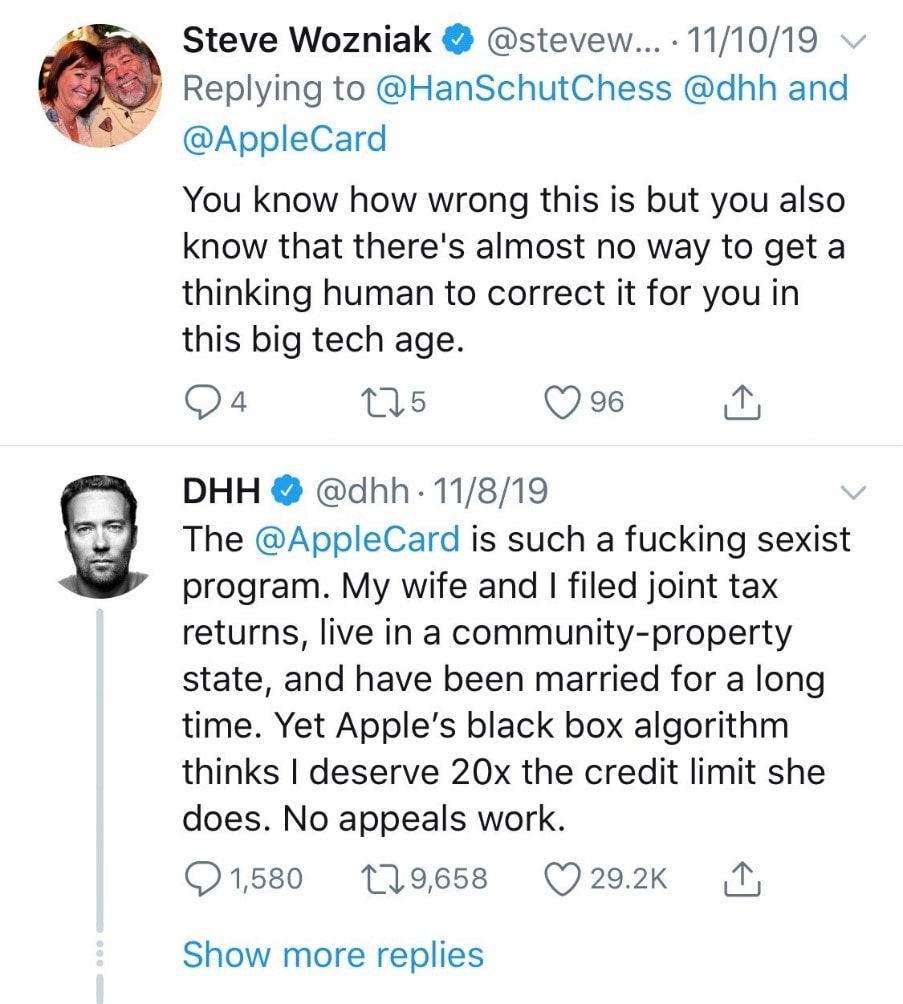
Apple was in a bit of a mini-scandal in the past few months. One of the entrepreneurs in the US and his wife shared all of the bank accounts, and his wife has a higher credit score than him. And they applied for a credit card, and he got a credit limit that was 20X higher than his wife. And all hell broke loose. He tweeted it and now the New York Department of Financial Services has commenced an investigation into this. To add fuel to the fire Steve Wozniack who is the co-founder of Apple, retweeted it saying that he was also in same situation. Companies need to think deeply about the decisions that their algorithms are making.
In AI ethics, are we behaving in the right way towards our customers? Are we misusing the trust? Are we misusing the data that our customers are willingly sharing with us?
Leveraging AI with Transparency
For example, let’s take the case of a health insurance company, that now has access to social media information of a patient – Naresh. Naresh regularly posts about his social life on Facebook and Twitter.
So the insurance company now has a moral dilemma, which is ‘Naresh is a high-risk patient, should I increase his premium, or should I discard this information?’. In this case, it is important to be transparent about how the company arrives at premium of their insurance products. Customers should be made aware that public information about themselves might be tracked to arrive at a more appropriate premium for the products they choose.
AI models don’t explain how they arrive at each decision they make. Although some vendors have introduced new explainable AI capabilities, most are using it for marketing purposes. Organizations do and will continue to achieve a lot of fantastic results without the need for full transparency.
Depending on the business context, however, privacy, security, algorithmic transparency, and digital ethics requires companies to bring in transparency into their business practices.
For example:
So in conclusion: