Home > Blogs > Cloud computing
Cloud computing

We all have heard or felt being “on cloud nine”. But what is business or software on the cloud? Why should we move to the cloud, probably these questions have already come to your mind? Some of you might be already working on cloud, either for business or personal use. Let’s go through some more details.
What is a cloud?
The term cloud refers to accessing a variety of computing services like servers, storage, software, databases and more over the Internet. Many of us have used taxi services like Ola or Uber. People book a taxi to the required location and pay for the distance traveled. Similarly, users can subscribe to the cloud services pay-as-you-go basis and select the type of cloud service like selecting the type of car. As booking a car is convenient, it’s easier to use the cloud services rather than building own infrastructure/software platforms etc.
Cloud service providers (CSP) are companies that offer cloud services. Some of the commonly used cloud services are Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft Office 365, and Apple iCloud mail etc.
Cloud Computing Models
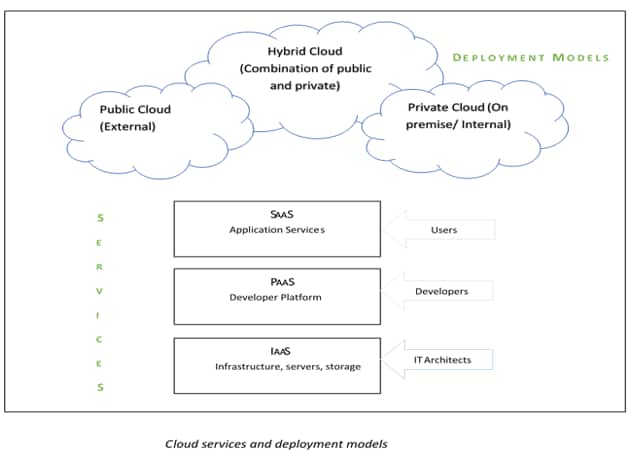
Cloud services are broadly categorized as follows:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides computing infrastructure or the actual hardware (servers and disks). With IaaS, users are responsible for installing all the required software on top of the hardware. Some of the popular IaaS products are Amazon EC2, Windows Azure, and Google’s Compute Engine (GCE).
¬Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers all the hardware along with the required platform. It provides a platform for developing, testing, deploying applications making developers life easy to build apps, without worrying about managing application environment. Popular PaaS platforms are IBM BlueMix, Heroku, Google’s App Engine, and Red Hat’s OpenShift. The oecloud platform of Edgeverve offers PaaS platform.
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers readymade application services built on top of the required platform and hardware. Some of the popular products are Google Docs, Dropbox, Office365, and Salesforce CRM application etc.
Cloud Models
Now let us look at the types of cloud deployment models.
Public cloud offers computing services to the public over the Internet using shared IT infrastructure and resources. Users are charged as per usage. Examples are Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Services.
Private cloud is private deployment option for an individual company which could be hosted on premise or externally by the cloud provider exclusively for individual business.
Hybrid cloud provides the combination of public and private models providing flexibility in moving data and applications between private and public cloud based on the business needs.
Cloud containers
Containers provide a lightweight environment to run applications with isolation boundary. Unlike virtual machines, they don’t need a full OS within the container, multiple containers can run on the same host. Containers are popular in PaaS to manage applications. Microservices are best fit for containerization as they can be independently deployed as containers, scaled up or down. Docker is one of the popular open-source container technologies. There are other platforms like ¬¬Google’s Kubernetes, Warden from Cloud Foundry, and Rocket from CoreOS.
Why move to Cloud?
Why this shift, definitely because of the edge it gives to the business compared to the traditional software.
Focus on business: Building the IT infrastructure from scratch and maintaining is expensive. With cloud services, maintenance and security of IT systems are taken care by the CSPs.
Availability: Most cloud providers are extremely reliable in providing their services with very minimal downtime. Users can access the services anywhere anytime with internet connectivity.
Cope with demand: Flexible payment options are available like pay-as-you-use or fixed subscription fee. Depending on the business demand capacity can be added or removed.
Go Green: As CSPs host multiple customers on shared infrastructure, data centers are optimized for energy efficiency.
Backup and Recovery: Most cloud providers have excellent backup and recovery mechanism.
Challenges
In spite of all the benefits, there are some concerns regarding the cloud. As data is accessible over the internet, a data breach could occur via hacking or any vulnerability attack. Reliable internet connection is a must for the business. Some of the providers use proprietary software/hardware, switching to another vendor becomes a costly affair. Companies should thoroughly analyze the pricing plans and service contract considering future expansion plans.
Summary
Cloud is evolving at a fast pace, with wider adoption by various companies. Like everything else, cloud computing has its own pros and cons and some of the current challenges may no more be a matter of concern in the coming days.
What are your views on cloud computing? Please leave your comment.
Leave a Reply
6 thoughts on “Cloud computing”
-
Like!! Thank you for publishing this awesome article.
-
Some genuinely nice and useful information on this website, besides I think the pattern has wonderful features.
-
Very nicely articulated Blog Rekha, very nicely covered the architecture.
-
A good article!
-
Nicely articulated#8230;Great info about basics of cloud..!!
-
Nice one. Very informative on cloud basics.
Load more comments...


Rekha Srinivas
More blogs from Rekha Srinivas >