Home > AssistEdge > Blogs > Unlocking the potential of RPA through Complementary Technologies – Intelligent Document Processing
Unlocking the potential of RPA through Complementary Technologies – Intelligent Document Processing

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the fastest-growing enterprise technology across industry segments, and its pace will continue to be substantial in 2020-21. It’s a style of automation where a software program mimics human actions to accomplish various tasks following a set sequence or flow. RPA is revolutionizing the way operations are run across the industry segments, be it Financial Services, Manufacturing, Logistics, or Healthcare. RPA robots can work 24*7, generating output with higher consistency and control, thus providing higher predictability in terms of outcomes. It has found its application across functional areas of the businesses, be it customer support, finance, HR, or purchase department. RPA helps take away the mundane and repetitive work from the human workforce, thus allowing them to focus more on the tasks which require human qualities like empathy and judgment.
Evolution of RPA
RPA has been around us in some shape or form since the 90s; initially, it was more a web scraping technology used for simple data extraction from web-pages. Later it obtained the elements of workflow embedded in it with the advancement of workflow technologies. In recent years with the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), RPA is moving to become more of a cognitive technology, which can not only mimic human actions but can also apply basic intelligence to deliver the results. Today, RPA has made rapid inroads into an organization’s technology roadmaps by virtue of being low code, easy to adopt, and faster to deliver technology solutions.
The emergence of Document Processing as a key force multiplier
As the adoption of RPA increased across industries, most of the organizations began piloting RPA projects in the areas where they already had legacy automation through Excel Macros or other older assisted automation technology. These RPA implementations helped them validate the compatibility of RPA technology within their organization setup. Post success of initial implementations, technology and operations teams moved quickly to identify more areas for RPA and started running multiple RPA processes across different functional areas, using core RPA capabilities of automating tasks.
Organizations across the globe still have many processes that involve the handling of documents, like Know Your Customer (KYC) in banking, claim processing in insurance or invoice processing in manufacturing. It was critical for the success of RPA that it go beyond automating the process, dealing with just interactions and data manipulation between multiple applications, and include the element of document processing.
As per Gartner’s latest report, by 2022, 80% of RPA-centric automation implementations will derive their value from complementary technologies. These complementary technologies include process mining, intelligent document processing (OCR, Computer Vision), Machine Learning & User experience. Gartner refers to the collective functionality as “Complemented RPA” (CoRPA).
Out of these complementary technologies, one of the fastest adaptations are in the area of Intelligent Document Processing. When it comes to converting documents into a machine-readable format, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is the answer. OCR refers to the process of converting different types of data, including PDF files, printed documents, or images into editable, accessible, and searchable formats for computers. OCR can help in reading bank statements, purchase agreements, or any other business document and deliver it in a machine-readable format for consumption by another software like RPA.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine learning (ML) in OCR has resulted in the emergence of technologies such as Computer Vision, Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) & Natural Language Processing (NLP). These new technologies contribute to making document processing more efficient and reliable. Now with intelligent document or image processing capabilities, RPA can extract information from any complex document which contains unstructured data, with a higher level of confidence in the output generated and then use it as an input for further processing. Organizations can easily automate processes involving documents like invoices\agreements\statements utilizing a combination of intelligent document processing tools and RPA to achieve end-to-end automation.
Let’s look at an example to understand the implementation better. A leading manufacturer works with multiple suppliers to source the input for its products. All the suppliers have entered into a contract with the manufacturer, which is then sent to the manufacturer’s purchasing department over emails (as PDF attachments). The purchase department has automated the process of inputting the contract key data from the contract into its SAP-based purchase management application. The organization has deployed XtractEdge Computer Vision along with AssistEdge RPA Albie Decision Workbench to achieve this automation. As the contracts received from the suppliers are not in a standard format, XtractEdge applies its computer vision capabilities to extract the key data elements from the contracts. Post data extraction, a confidence score is generated, which is pushed as input to AssistEdge RPA Albie bot. AssistEdge RPA Albie bot, based on the confidence model threshold, either sends the contract information directly to the SAP system or moves it to decision workbench as a task for the human worker to review and approve it to be fed into the SAP system. This brings in the element of “Human in Loop” in the automation, thus making it a more resilient and controlled implementation.
The above process creates a viable ecosystem for human-empowered automation, thereby helping the enterprise attain ‘Automation Singularity Led by Humans.’
Automation Singularity refers to a highly customer-centric and agile oriented state of constant improvement and optimization through the future workforce, opening an expanded horizon of possibilities. Human specialists drive customer orientation using their creativity and empathy and are complemented by digital workers with extreme productivity and consistency.
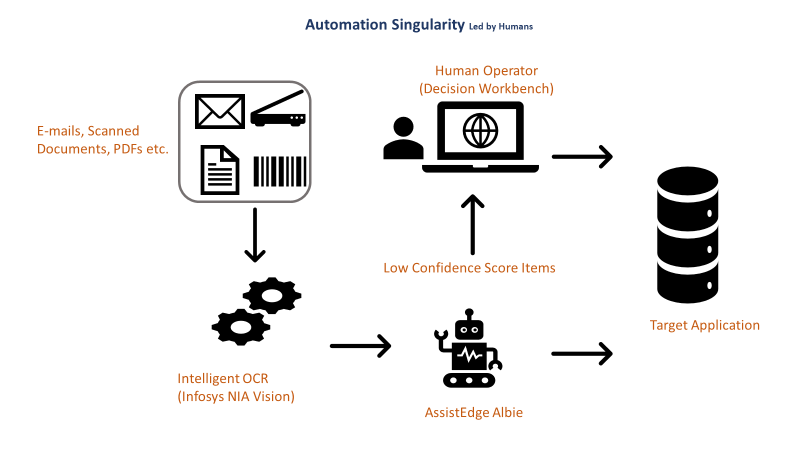
Thus, the future of RPA-driven automation lies in taking it beyond vanilla task-based implementation, to one incorporating human-empowered complementary technologies.
Reference:
OCR: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_character_recognition
Computer Vision: https://www.edgeverve.com/assistedge/blogs/computer-vision-enable-data-collection/
Gartner Predicts 2020: RPA Renaissance Driven by Morphing Offerings and Zeal for Operational Excellence
Automation Singularity: https://www.edgeverve.com/assistedge/blogs/redefining-intelligent-goals-automation-singularity/


Vishal Swami
Product Manager, EdgeVerve
More blogs from Vishal Swami >