

Data is the new oil fueling the digital economy, but its flow is threatened by data privacy regulations and AI-driven platforms. How can businesses protect personal data throughout its lifecycle and include data privacy and security in their digital transformation efforts? Find out why a centralized privacy policy is crucial and how identifying vulnerabilities and building data privacy into workflows can unlock the true potential of your enterprise in the digital age.
While oil was one of the most critical resources of the industrial age, data is now powering the engines that the digital economy is progressing on. The internet, the backbone of the digital economy, is seen as the new oilfields with IOT, automation, AI/ML and other emerging technologies providing the refining process to transform raw data into valuable insights that power decisions.
For the past decade, digital transformation has been a critical item on every CXOs agenda. The digital transformation initiatives generate data about products, services, and customers, helping organizations predict trends and take decisive actions to improve customer experience and increase customer satisfaction.
Data Privacy Regulations
Governments and regulatory authorities focusing on data privacy and personal information protection mandate privacy regulations and strict control. These drive large organizations with data-driven operations to start their privacy program efforts.
A Gartner prediction1 states that 75% of the global population will have personal data covered under privacy regulations, with large organizations’ average annual budget for privacy exceeding $2.5 million by 2024.
Businesses and consumers interact through social media platforms that collect large amounts of personal data. Further, with the help of AI-driven platforms, data is being processed to create new engines that serve as filters and controls for privacy-enhancing technologies. While these technologies are increasing the rate of innovation and adoption of new ways of existence, they pose a significant risk to data privacy.
Individuals are asking for more control over the information collected about them and how it is used, who can access it, and how the organizations collecting the information protect their personal information. Organizations must build trust in individuals about their data privacy measures and how their data is handled within the system.
Data is a valuable company asset, and protecting it by identifying vulnerable points throughout the lifecycle is crucial. Data privacy risk is defined as the potential harm that the violation of personal data can cause. Data is most susceptible at five key stages – collection, storage, sharing, analysis, and deletion – and a data breach at any stage can prove quite costly.
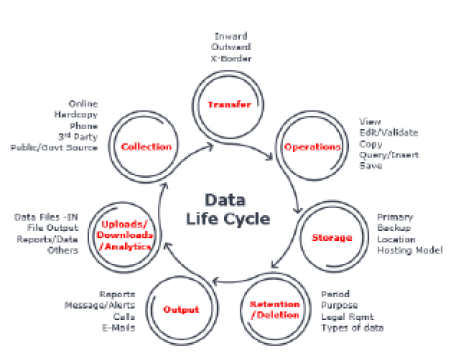
Let’s understand what the difference between data privacy and security is. They vary primarily in whom or what they are protecting personal data from.
Data Privacy prioritizes the individual’s rights in deciding how their personal information is handled, processed, stored, and used. Data Privacy ensures that the way personal data is processed, stored, or transmitted by any business complies with regulations and has consent from the owner of that sensitive data.
Individuals and end-users demand more privacy, including clarity, choice, and authority over how businesses collect and use their data, resulting in the digital ecosystem including multiple data privacy tools. Data Privacy tools include browser extensions and add-ons, password managers, and other services that help block websites, internet browsers, cable companies, and internet service providers from tracking personal information and history. This forces businesses to rely on data gathered directly from customers for further processing.
Data Security focuses on securing and protecting personal and sensitive data from unauthorized access or exploitation by third parties. Data security is a prerequisite to data privacy, setting the policies, methods, controls and means necessary to secure personal data. Data Security controls include identity and access management, data loss prevention, anti-malware, anti-virus, event management and data masking software that helps protect data from compromise by malicious actions of both internal and external parties.
With the increasing risk of data privacy, organizations need to include the building blocks of data privacy and security as part of business innovation and digital transformation to protect personal data at every stage of the data life cycle. Enterprise IT teams must implement technical and process controls at different system layers to ensure that personal and sensitive data is secure, and privacy is respected.
Loved what you read?
Get practical thought leadership articles on AI and Automation delivered to your inbox


Loved what you read?
Get practical thought leadership articles on AI and Automation delivered to your inbox
As enterprises are expanding globally, data is being shared across borders. Global organizations are implementing privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) to protect and secure sensitive data. Government regulators are also promoting the use of PETs and are developing frameworks that assess the impact of these technologies on data access and availability. However, it is eventually the responsibility of the enterprises to ensure that their technology platforms comply with data privacy regulations and privacy policies that are in force in the specific geography and industry.
There is a continuous evolution in how businesses collect, process and use data with corresponding advancements in data security, privacy, access processes and regulations. As data volumes and sources continue to grow, rules will become more stringent to ensure the safety and protection of personal data.
Disclaimer Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the respective institutions or funding agencies





