VLookup Range
VLookup Range feature enables you to automatically implement the VLOOKUP feature of the Excel application. It enables you to lookup for a value in one column of a table and fetch the matched data against the lookup value from another column.
Using VLookup Range Feature
- Make sure the prerequisites for using Office 365 activities are met.
- In the Canvas Tools pane, click Office 365 Services to expand the tool and view the associated activities.
- Drag the Excel 365 activity inside the Office 365 Application Activity. Ensure that the output token of the OAuth process is passed on to the Excel activity for authentication. For more information, see OAuth Activity.
- The validation error symbol disappears when you select relevant values in the particular field from the available list. For example, Access Token, Append Range, and Output.
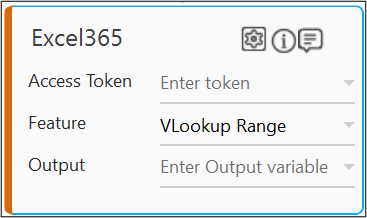
- The validation error symbol disappears when you select relevant values in the particular field from the available list. For example, Access Token, Append Range, and Output.
- In the Access Token list, select the output parameter holding the value of access token from the OAuth activity to pass in the Excel 365 activity. For more information, see OAuth activity.the Feature list, select Read Table Row.
- In the Feature list, select VLookup Range.
- Click the
 (Setting) icon to configure the input parameters. The Input Configuration screen appears.
(Setting) icon to configure the input parameters. The Input Configuration screen appears.
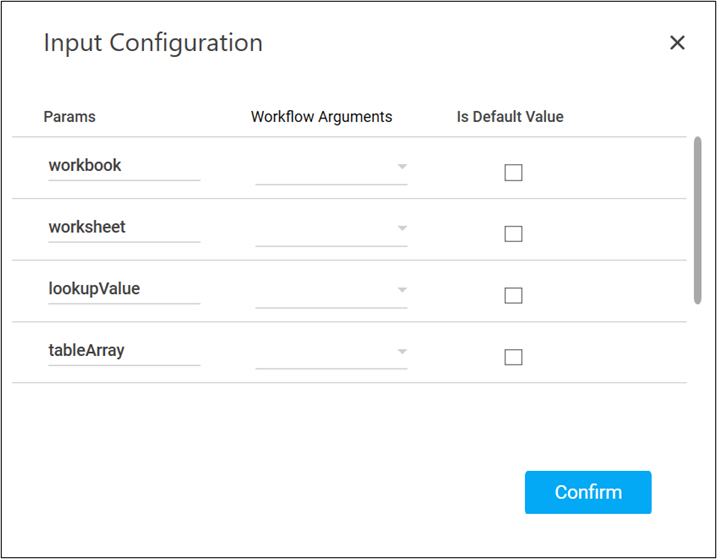
- Ensure to define all the input parameters as an In argument in the Argument bar for selection in the mandatory options.
VLookup Range feature does not have any optional parameters to define. - You can select the Is Default Value checkbox to set the selected input parameter as the default value.
- Mandatory Options:
- Corresponding to the workbook parameter, select the argument holding the workbook path along with the workbook name and its file extension. For example, RDtest\EmployeeDetails.xlsx.
If the excel file is present at the root folder location, you must define only the workbook name and its file extension. For example, EmployeeDetails.xlsx. - Corresponding to the worksheet parameter, select the argument holding the name of the Excel sheet from which you want to fetch data implying VLookup Range feature.
- Corresponding to the lookupValue parameter, select the argument holding the value to look for in the column of the table.
NOTE:
You cannot directly pass the cell reference or the index number as the value of the argument for the lookupValue parameter. However, you can use the Read Cell feature to fetch and pass the required cell value to the VLookup Range feature. - Corresponding to the tableArray parameter, select the argument holding the range of cells to search for the required data. For example, b1:c5. Here b1 signifies the column where the lookup value is located and c5 is the last column until where the search must be done.
- Corresponding to the colIndexNum parameter, select the argument holding the column index in the table from which data must be fetched.
NOTE:
The column indexing starts from 0. It signifies that if you want to fetch data from the 3rd column of the specified table, you must enter the column index number as 2. - Corresponding to the rangeLookup parameter, select false if you want to fetch the first match; else, select true if you want to fetch the last match.
- Corresponding to the workbook parameter, select the argument holding the workbook path along with the workbook name and its file extension. For example, RDtest\EmployeeDetails.xlsx.
- Mandatory Options:
- Click the
- Once done, click Confirmn.
- In the Output dropdown list, select an Out argument which should store the result. The argument should be of Out Direction.
- Save the process.
- In the Tool bar, click Setup Environment.
- Once environment setup is completed perform the Test Run.
The VLookup Range feature is configured.
The fetched data is in the array format. Following is the sample output received:
{“Value “:”Florida”}