Excel Applications
This activity allows you to automate the redundant and tedious task performed on an excel application such as reading and writing data, data extraction and migration, comparing data in columns or rows, executing analysis reports, integrating with other applications and databases and so no.
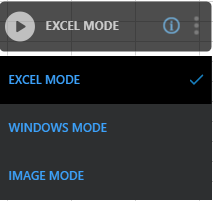
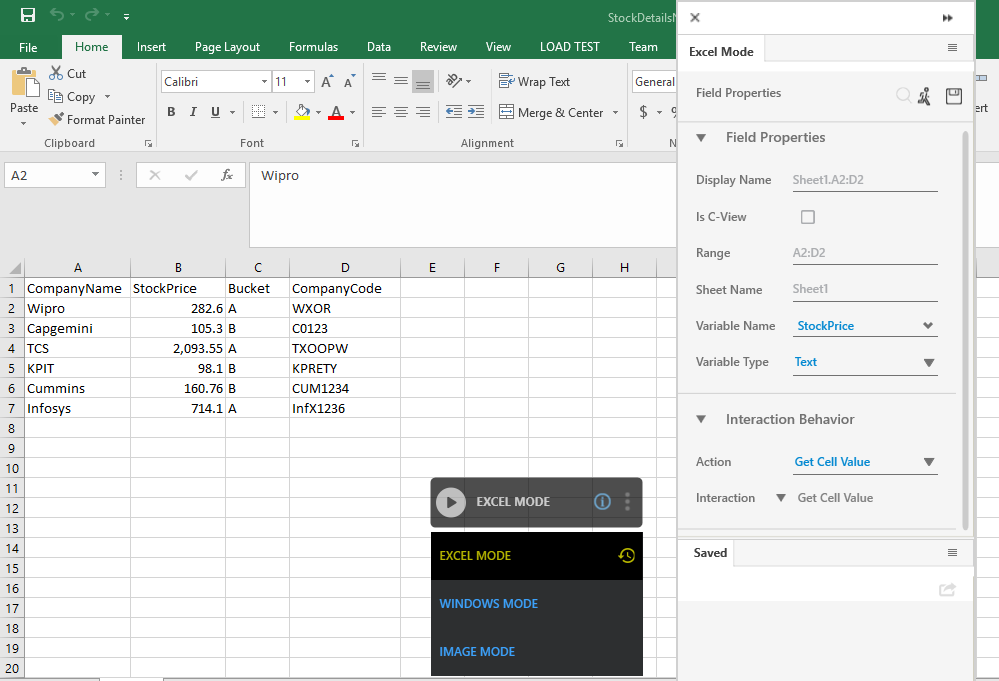
You can automate the cells and worksheet of the excel file using the EXCEL MODE of the Multimodal Interface. Additionally, WINDOWS MODE and IMAGE MODE are available which is useful to automate the ribbon and menu controls of the excel file.
Configuring Excel Application
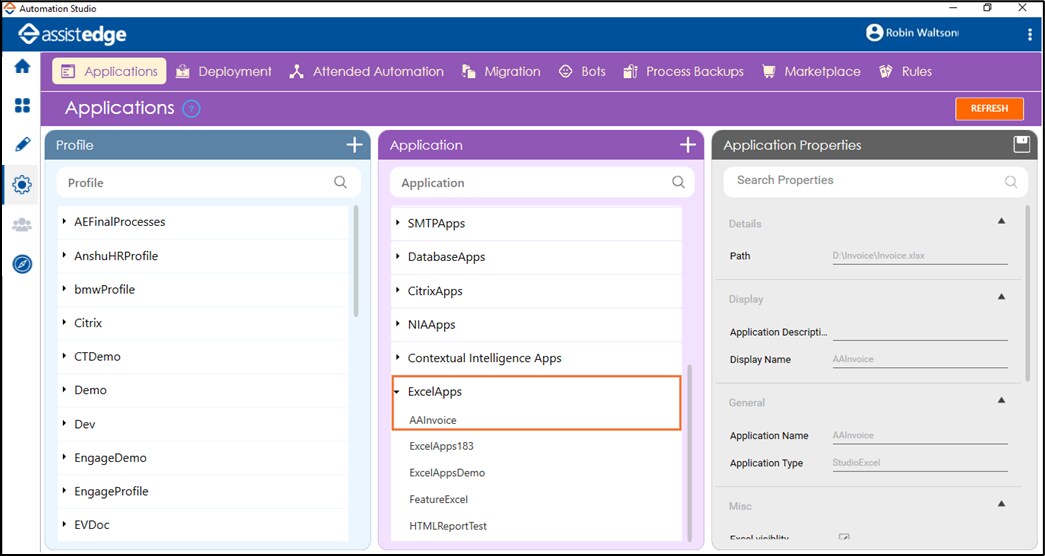
Configure the excel application in Automation Studio where you want to perform the automation. Below are the minimum required properties for configuring the intended excel application. If you want to define remaining properties, refer ExcelApps in the Admin Menu.
- In the Admin menu, add an application of Application Type- ExcelApps. The Add Application dialog box opens.
- In the Application Name field, enter a desired name of excel application you want to add. The name must not contain any special character or space.
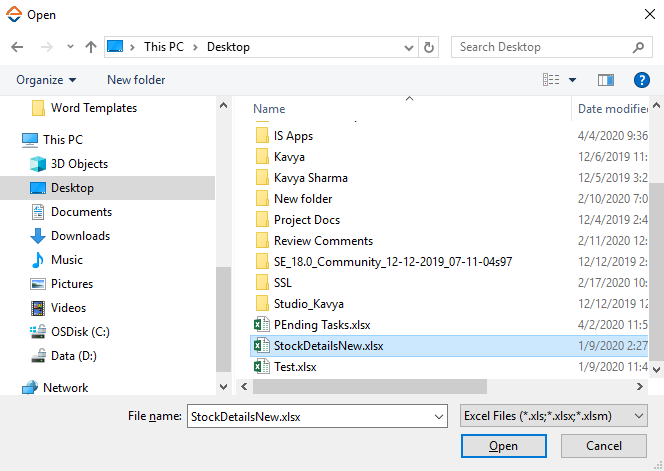
- Click ADD and browse for the excel file you wan to configure. Click Open.
The excel application is configured.
Using Excel Application Activity
- In the Canvas Tools pane, click Process Components to expand the tool and view the associated activities.
- Drag the Application activity and drop on to the Flowchart designer on the Canvas.
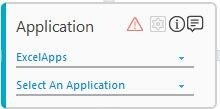
- From the Application Type list, select ExcelApps. You must have at least one application added for it to appears in the list. See Admin Capabilities to know how to add application before using an activity.
- In the Select An Application list, select the configured excel file that you want to automation. Alternatively, you can a add a new excel application at this point of time. To add an excel file:
- In the Select An Application list, click Add New Application. The Add New Application dialog box appears.
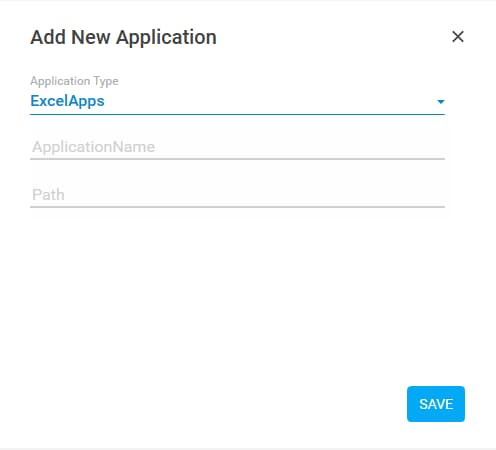
- In the Application Name field, enter a desired name of the application.
- In the Path field, enter the path of the excel file (along with the file name) available on the system.
- Click SAVE. The excel file is added.
- In the Select An Application list, click Add New Application. The Add New Application dialog box appears.
- Click the
 (Settings) icon to launch the EXCEL MODE interface. The configured excel file appears along with the EXCEL MODE interface.
(Settings) icon to launch the EXCEL MODE interface. The configured excel file appears along with the EXCEL MODE interface.
- Click the
(Play) icon, to start capturing the automation steps that you want to perform within the excel file. The Play icon changes to the
 (Recording) icon. You can switch among EXCEL MODE, WINDOWS MODE and IMAGE MODE based on the requirement.
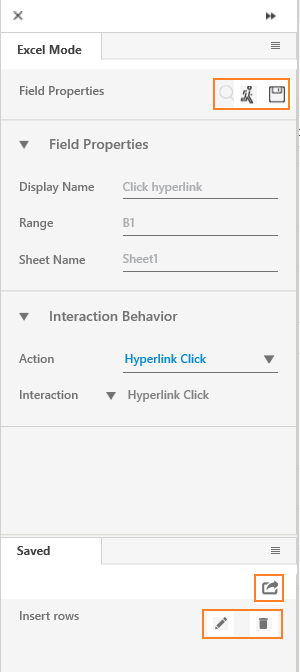
(Recording) icon. You can switch among EXCEL MODE, WINDOWS MODE and IMAGE MODE based on the requirement. - Click the area that you want to capture as part of the automation process workflow. The Field Properties panel of the Excel Mode appears. The fields that are mandatory are highlighted with red box.
- In the Action list, select the action that you want to perform on the captured area. Other mandatory fields changes depending on your selection from the drop down list.
Enter details of all the mandatory fields and other relevant fields as per your requirement. - Click the
(Save) icon to configure the fields.
- Repeat steps 6 through 10 to capture all the steps involved in the automation process workflow. With the help of
 (Run Now) icon, you can perform the action related to the configured field to see if the intended configuration is done.
(Run Now) icon, you can perform the action related to the configured field to see if the intended configuration is done.
The field that you configured and saved appears in the Saved pane of the Field Properties panel. You can edit or delete these steps in the Saved pane.
- Click the
(Save configured field and return to studio) icon to save the field that you configured and return to the Studio menu.
The fields are configured and the Application activity for Application Type- ExcelApps is created.
Excel Mode Field Properties
The properties of Excel Mode fields are listed in the following table:
|
Property Name |
Usage |
|
Field Properties |
|
|
Display Name |
User specified display name of the excel element selected. |
|
Range |
A single cell or the collection of cells where the intended action must be performed. It can be collection of two or more cells and not necessarily to be adjacent to each other. |
|
Sheet Name |
The name of the excel sheet to perform the action. |
|
Interaction Behavior |
|
|
Action |
Actions that can be performed on the excel application. Available options are:
|
|
Interaction |
The corresponding interaction set against the selected action. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Get Cell Value and Search. |
|
|
Is C-View |
If selected, the field configuration captured in Automation Studio is visible in the C-View tab of Engage application. |
|
Variable Name |
User defined name of the variable that stores the captured value. |
|
Variable Type |
Type of the variable defined. Available options are:
|
|
Appears if Action selected is Run Macro. |
|
|
Macro Argument |
The arguments which you need to pass to the macro to execute. |
|
Macro Name |
The name of the macro that you want to run. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the macro as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Macro Name field and then enter the name of the macro if you want to pass the macro as a default macro. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Paste. |
|
|
Paste Option |
The options to paste content in the excel sheet. Available options are:
|
|
Appears if Action selected as Search. |
|
|
Search Type |
The type of search you want to perform in excel sheet. Available options are:
|
|
Search Range |
The criteria to select the range to search for the required content. Available options are:
|
|
Search Value |
The content for which the corresponding value must be searched based on the Search Range field. |
|
Search Location |
The row or column name where the search must be done. |
|
Fetch Result From |
The row or the column name corresponding to the Search Location field from where the search value must be retrieved. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Set Text. |
|
|
Column Separator |
The separator to insert the values in the column. |
|
Data to insert |
The value that you want to set in the selected cell or range of cells. The values are inserted based on the defined Column Separator or Row Separator. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the values as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Data to insert field and then enter default values with a defined separator. |
|
Row Separator |
The separator to insert the values in the rows. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Insert Column. |
|
|
Column |
The default column name where the new column would be inserted. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Insert Column. |
|
|
Row number |
The number of the row where the new row would be inserted. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Remove Duplicate. |
|
|
Column |
Define the index of the required column. For multiple columns, separate the indexes with delimiters. By default, the delimiter is defined as comma (,). Note: The indexing of the column is dependent on the Range selected in Field Properties. If the range is selected as C:E and you want to remove duplicates from column D, then the indexing for column D is 2. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the column index as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Column field, and then enter pivot column index if you want to pass the column as default. |
|
Has Headers |
Select the required option from the list. The available options are:
|
|
Index Delimiters |
Delimiters are used to separate multiple indexes defined in the Column field. By default, the delimiter is defined as comma (,). You can change a predefined delimiter if required. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Rename Worksheet. |
|
|
Rename Sheet as |
Specify the new name for the worksheet. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the name as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Rename Sheet as field, and then enter the name of the sheet if you want to pass the sheet name as default. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Refresh Pivot. |
|
|
Refresh All |
Select this option to refresh all the available pivot tables in Excel file. |
|
PivotTable Name |
Specify the pivot table name. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the pivot table name as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the PivotTable Name field, and then enter pivot table name if you want to pass the pivot table name as default. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Sort Data. |
|
|
Has Header |
Select the required option from the list. By default, it is set as Guess. The available options are:
|
|
Sort Order |
Select the sorting order for a specified column from the list. By default, it is set as Ascending. The available options are:
|
|
Sort Worksheet |
Select this option if you want to move the entire row with the specified column. This option retains the data intact in specified Excel sheet. |
|
Sorting Column |
Define the column name for sorting. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the sorting column as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Sorting Column field and then enter the column name if you want to pass the column as default. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Auto-fill Data. |
|
|
Autofill Type |
Select the auto-fill type from the list. By default, it is set as Default. The available options are:
|
|
Destination Range |
Define the cells start point and endpoint. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the destination range as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Destination Range field and then enter the required range if you want to pass the destination range as default. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Copy Worksheet. |
|
|
Copied SheetName |
Define a name for the copied sheet or use as default. If named as default, then the functionality will work as per Microsoft Excel. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the sheet name as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Copied SheetName field, and then enter the name of the sheet if you want to pass the sheet name as default. |
|
Target Workbook |
Define the path of the targeted Excel file if you want to copy the sheet in a different workbook. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the targeted workbook as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Target Workbook field, and then enter the path of the targeted Excel file if you want to pass the targeted workbook as default. |
|
Appears if Action selected is Delete Operations. |
|
|
Delete Row |
Deletes entire row at the specified location in Excel sheet. |
|
Delete Column |
Deletes entire column at the specified location in Excel sheet. |
|
Delete Range |
Deletes cells at the specified location in Excel sheet. Select the behavior which is executed after deleting the selected range. There are two types of behavior available in the Shift Action list.
|
|
Appears if Action selected is Add DataTable. |
|
|
DataTable |
Define the data table name. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the data table name as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the DataTable field, and then enter the data table name if you want to pass the data table as default. |
|
Include Headers |
Select this option if headers need to be copied in the specified Excel sheet. |
|
Data Type |
Select the data type from the list. By default, it is set as Number. The available options are:
|
|
Number Filter |
Select the filter from the list for the number data type. By default, it is set as Equal. The available options are:
|
|
String Filter |
Select the filter from the list for string data type. The available options are:
|
|
Column Number |
Specify the required column number to apply filters in that particular column. The column number starts from 0. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the value as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Column Number field, and then enter the column number if you want to pass the column number as default. |
|
Filter Value |
Define a value for the filter. You must define a parameter in the Parameter bar if you want to pass the filter value as an argument or as a variable. Select the check box beside the Filter value field and then enter filter value if you want to pass the filter value as default. |
Excel Application Properties
The properties of an excel application are listed in the following table and can be edited in the Property grid on the right pane.
|
Property Name |
Usage |
|
Control Execution |
|
|
Ignore Error |
When this option is set to Yes, the application ignores any error while executing the activity. If set to NA, it bypasses the exception (if any) to let the automation flow continue; however, it marks the automation status as failure, in case of an exception. By default, this option is set to No. |
|
Delay |
|
|
Wait After |
Specify the time delay that must occur after the activity is executed. The value must be in milliseconds. |
|
Wait Before |
Specify the time delay that must occur before the activity is executed. The value must be in milliseconds. |
|
Misc |
|
|
Breakpoint |
Select this option to mark this activity as the pause point while debugging the process. At this point, the process freezes during execution allowing you to examine if the process is functioning as expected. In large or complex processes, breakpoints help in identifying the error, if any. |
|
Commented |
Select this option to mark this activity as inactive in the entire process. When an activity is commented, it is ignored during the process execution. |
|
DisplayName |
The display name of the activity in the flowchart designer. By default, the name is set as the name of the selected application. You can change the name as required. |