Python Script
This activity lets you automate an existing Python script that helps you complete a specific task in lesser time such as efficiently achieve web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence and any other task that has been designed using the Python script.
Prerequisite
You need to install Python (v3.6) on the systems where the robots run and also on the system where the Python scripts are developed. Configure the path of the .exe file of the Python as an Environment Variable- PYTHON_PATH.
To configure the path of the .exe file of Python as Environment Variable:
1. In the Start menu of the required system, enter Edit the system environment variables.
NOTE: |
· You need the system administrator rights to edit a system environment variable. · If you do not have administrator rights, use environments variable for your account. If you configure the environment variable using your account, other users would not be able to execute the activity. This can be done for development and testing purposes. |
2. Double click and open the displayed app. The System Properties dialog box opens.
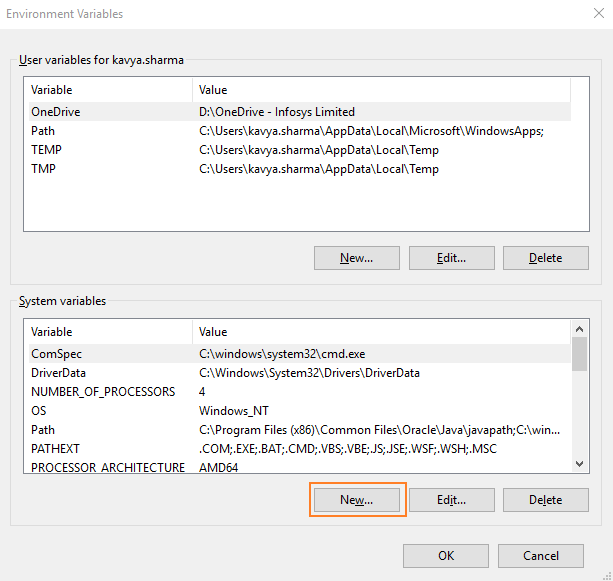
3. Click the Advanced tab, and then click Environment Variables. The Environment Variables dialog box appears.
4. In the New System Variables dialog box, enter PYTHON_PATH in the Variable name field.
5. In the Variable value field, enter the path of the .exe file of the Python is installed on the system. For example, C:\Programs Files\Python36.
6. Click OK.
The path of the .exe file is configured as Environment Variable and starts appearing in the system variables' list.
Using Python Script Activity
1. In the Canvas Tools pane, click Process Components to expand the tool and view the associated activities.
2. Drag the Python Script activity and drop on to the Flowchart designer on the Canvas.
3. Click Add Script to browse and select the Python script to be executed.
4. Click
the ![]() (Settings)
icon. The Input Parameters
dialog box opens. It lets you add input parameters, if required
for the script to execute correctly. The type of input parameters
supported are :
(Settings)
icon. The Input Parameters
dialog box opens. It lets you add input parameters, if required
for the script to execute correctly. The type of input parameters
supported are :
· InArgument<Int32> |
· InArgument<Double> |
· InOutArgument<String> |
· InArgument<Int64> |
· InArgument<Decimal> |
· InOutArgument<DateTime> |
· InArgument<String> |
· InOutArgument<Int32> |
· InOutArgument<Double> |
· InArgument<DateTime> |
· InOutArgument<Int64> |
· InOutArgument<Decimal> |
Named or unnamed input parameters can be passed to the selected Python script. For example, in the input parameter - addtwonos.py 1 2, 1 and 2 are the unnamed parameter passed to the script while in the input parameter - addtwonos.py --a 1 --b 2, a and b are the input parameters and their respective value 1 and 2 are the named parameters. The -- is the delimiter separating the input parameters.
5. Click Add to add a new row.
6. In the Delimiters list, select the required separator to separate the named parameters. Available delimiters are, - and --. If a single named input parameter is passed, the delimiter is ignored.
7. In the Parameter Name field, enter a desired name of the input parameter.
8. In the Parameter Value list, select the parameter holding the value of the input parameter that needs to be passed to the script. You must define the parameter in the Parameter bar to make it available for selection in the list. Only In and InOut parameter types are displayed in the list. If the input parameter needs to be populated by other activity, the parameter type must be InOut.
9. Select the IsNamed check box, if the input parameter is a named parameter.
10. Repeat step 5 through step 9 to add the required input parameters.
11. Click CONFIRM to save the details.
12. In the Properties pane of the Python Script activity, select the Out parameter in the PythonOutputParam field which is used to store the output if the script returns any value. It can be used as an input for an action that you want to perform in the automation process workflow. You must define the parameter in the Parameter bar to make it available for the selection.
The Python Script activity gets created with a default name.
Once the automation process workflow is executed the folder containing the Python script gets zipped and saved at the UserInstanceDirectory path defined in the Automation Studio.exe.config file. By default, the path is set to %localappdata% > EdgeVerve > $ParentDir$ > ProtonFiles > PyScripts folder and can be edited if required. A new zipped folder gets created every time the process is executed and a unique numeric string gets attached to the name of the zipped folder such as 092722c8-5321-4b06-bd9e-f72c83793225.zip.
The zipped folder is uploaded to the database after the automation process workflow is deployed. If you replace the script with another script in the activity, the same row in the database gets updated instead of creating a new row. The robot uses the Python script from the database to execute the process.
Dependency Management
All the dependencies of the specified Python script should be present in the same folder as the selected script in the activity. For example, if you have selected the test.py Python script present inside the D > PythonScripts folder, all other dependent files must also be present inside the D > PythonScripts folder. The activity zips the entire PythhonScripts folder and uploads the zipped folder to the database. The robot then uses the specified Python scripts and the related files present inside the zipped folder to execute the automation process workflow. The file not found error is received if the zipped folder gets deleted.
NOTE: |
You must not place the required Python script directly in any root drive folder such as the D:/ drive. The activity may not correctly identify the dependent files if the specified Python script is placed directly inside the root drive folder and uploads only the specified Python script. This leads to the failure of the automation process workflow. |
Related Topics